 A suspended licence means that you cannot drive for a specified amount of time. You regain the ability to drive after the suspension period ends, usually automatically.
A suspended licence means that you cannot drive for a specified amount of time. You regain the ability to drive after the suspension period ends, usually automatically.
A disqualified licence, on the other hand, means that you cannot drive at all. A disqualified licence occurs when a licence is cancelled. A cancelled licence essentially no longer exists. There is no automatic period when you get your licence back like a suspended licence. Instead, you must apply to get a new licence after it is cancelled, and you can often only apply after a set time.
Suspended Licence
The court can suspend your licence if you violate certain traffic laws. The suspension can be automatic in some cases, or it can be imposed as part of penalties associated with violating certain laws. The following violations will generally result in automatic suspension:
- Driving 45km/h or more over the posted speed limit
- Driving 145km/h or more in a speed limit zone of 110km/h (including a requirement for vehicle impoundment)
- Being charged with certain serious criminal offences, including murder, attempted murder, gross violence, or serious injury due to a motor vehicle
- Drinking and driving offences, including refusing to take a breath or drug test
A licence can also be suspended for failing to pay fines. It is not illegal to eat or drink while driving in Victoria, provided that it does not cause significant distractions or impair your driving ability. However, if eating or drinking leads to careless or dangerous driving, it can result in penalties. In general, this type of suspension is treated more leniently compared to other reasons for having your licence suspended.
Suspension periods can vary a great deal—from just a month or two to several years. In general, if your licence is suspended or disqualified in any state in Australia, you cannot drive in another state.
When an immediate suspension is imposed, a driver must turn over their licence to the police officer who issued the notice. In some serious cases, drivers may need to appeal to the Magistrates’ Court to get their licence reinstated.
Disqualified Licence
When a driver is disqualified, their licence is cancelled. A disqualified licence is often the result of a guilty finding involving the dangerous use of a vehicle. In fact, based on the Sentencing Act 1991, the court is required to cancel a driver’s licence if someone is found guilty or is convicted of a serious motor vehicle offence.
Below are a few minimum periods of disqualification for certain serious offences in Victoria. There is no maximum period of disqualification.
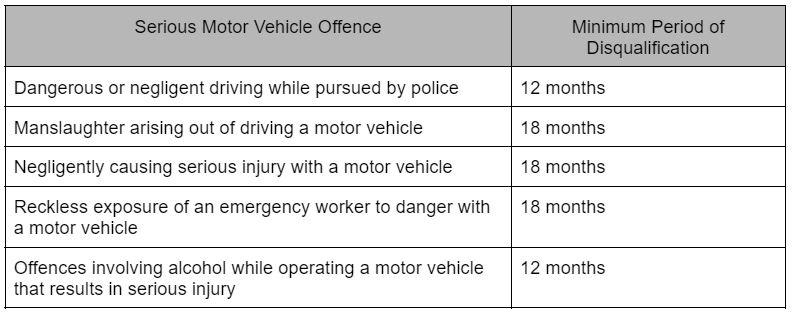
If a person has been disqualified from obtaining a driver’s licence or learner’s permit, they may need to apply to the Magistrates’ Court to become eligible for a licence.
If the disqualifying event was alcohol-related, then the driver may be required to obtain an alcohol interlock as part of the process to regain their full licence. In addition, those who were disqualified for alcohol must also have a zero concentration of alcohol present in their bloodstream while driving for at least the first three years of regaining permission to drive. That period may be longer if the court orders.
Consequences for Driving While Suspended
If someone is caught driving while suspended, they can face fines. If those fines are not paid, then a driver could end up in jail.
If you are caught driving on a suspended licence, then the maximum penalty is ten units. A unit is a measure used to determine the amount payable for a fine. The value of each unit between 1 July 2023 and 30 June 2024 is $192.31, which means the maximum penalty for this period is $1,923.10. The value of a unit is adjusted for inflation each year.
You can usually pay the fine outright, pay it by a certain date in the future, or request that the court put you on a payment plan.
Consequences of Driving While Disqualified
If you drive while disqualified, you may face immediate jail time. The maximum penalty is four months in jail for the first offence. The potential jail time increases for subsequent offences.
Conclusion
A suspended licence is less serious compared to a disqualified licence. In most cases, your licence will be reinstated after a suspension period. Licence suspension will often arise from excessive speed charges, certain serious criminal charges, and some drink-driving or drug-driving offences.
Licence disqualification arises when serious charges related to driving a motor vehicle occur. Drivers must apply to have their licence reinstated once it has been disqualified.
Regardless of which type of driving restriction you might be facing, speaking with a criminal defence lawyer about your rights and options may be a good idea.
Resources and Further Reading
- https://www.legalaid.vic.gov.au/driving-while-suspended
- https://www.legislation.vic.gov.au/in-force/acts/road-safety-act-1986/213
- https://www.vicroads.vic.gov.au/licences/drink-driving-drug-driving-and-excessive-speed-offences/immediate-licence-suspension
- http://classic.austlii.edu.au/au/legis/vic/consol_act/sa1991121/s89.html
- http://classic.austlii.edu.au/au/legis/vic/consol_act/sa1991121/s87p.html
- http://classic.austlii.edu.au//au/legis/vic/consol_act/ca195882/
- https://www.legalaid.vic.gov.au/penalty-units#:~:text=Penalty%20units%20are%20used%20to,2023%20to%2030%20June%202024


